Program Objectives & Support
Preceptors play a vital role in nursing education by bridging the gap between classroom learning and real-world clinical experience. In graduate nursing programs, their mentorship is essential to achieving key program objectives — including the development of advanced clinical judgment, leadership skills and evidence-based practice.
Graduate Program Objectives
- Integrate research, scholarship, and evidence based practice from nursing and related sciences as a framework for planning holistic care of the patient in various environmental contexts.
- Demonstrate competence in providing and evaluating advanced nursing practice with an emphasis on safety and quality.
- Demonstrate leadership for advanced nursing practice as a member of an interprofessional team within various environmental contexts.
- Design evidence-based clinical prevention and population care and services to individuals, families, and communities.
- Critically appraise evidence in the planning, delivery and evaluation of safe and effective care within various environmental contexts.
- Demonstrate knowledge and skills to promote health and help shape the health delivery system through policy, processes, and advocacy.
- Develop culturally sensitive, ethical, and financially sound comprehensive nursing care to individuals, aggregates, and/or communities.
- Apply concepts related to clinical prevention in developing and evaluating interventions and programs to address health promotion/disease prevention efforts
- Demonstrate leadership for the delivery of ethical, safe, cost-effective, high quality health care through expert collaboration, consultation, analysis, and administration
- Demonstrate the conceptual ability and technical skills to develop and execute an evaluation plan involving data extraction from clinical information
- Develop quality programs designed to improve health care of individuals, populations, or society through the use of multidisciplinary teams
- Formulate strategies for the development of institutional, local, or national health policy
- Integrate nursing science with knowledge from biophysical, psychosocial, political, economic, organizational, and analytical sciences as the basis for the highest level of nursing practice
- Provide and/or direct exemplary patient care within the scope of practice for the specialty
Support Team
- Program coordinator
- Academic advisors/student success coordinators
- MSN and Post-MSN Certificate programs: Angie Cook
- DNP program: Mike O'Neal
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program directors
- Post-MSN Certificate and DNP programs: Kim Mullins, DNP, APRN-CNP, AOCNP
- MSN program: Lindsay Davis, DNP, APRN-CNP
- Academic advisors/student success coordinators
- MSN program:Tara Straz
- Post-MSN Certificate and DNP programs: Mike O'Neal
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program directors
- MSN program: Jason Gregg, DNP, APRN, FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC, FIAAN
- Post-MSN Certificate program: Sherry Donaworth, DNP, APRN, ACNP-BC, FNP-BC, FPCNA
- DNP program: Jeff Trees, DNP, FNP-BC, CNP
- Academic advisors/student success coordinators
- MSN program: Kaitlyn VanWay
- Post-MSN Certificate program: Ashley Galinger
- DNP program: Mike O'Neal
- Clinical site coordinators
- MSN program: Melissa Joos
- Post-MSN and DNP programs: Taylor Soria
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Academic advisor
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Assistant program director
- Academic advisor/student success coordinator
- Program Manager
- Program director
- Academic advisor/student success coordinator
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Academic advisors/student success coordinators
- Certificate program: Mike O'Neal
- MSN program:Tara Straz
- Clinical site coordinator
- MSN program: Melissa Joos
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Academic advisor/student success coordinator
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Academic advisor/student success coordinator
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Academic advisors/student success coordinators
- Post-MSN Certificate program: Ashley Galinger
- DNP program: Mike O'Neal
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program director
- Academic advisor/student success coordinator
- Clinical site coordinator
- DNP program: Joe Letizia
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
- Program coordinator
- Academic advisor/student success coordinator
- Clinical site coordinator
- CastleBranch critical requirements administrator
State Authorization
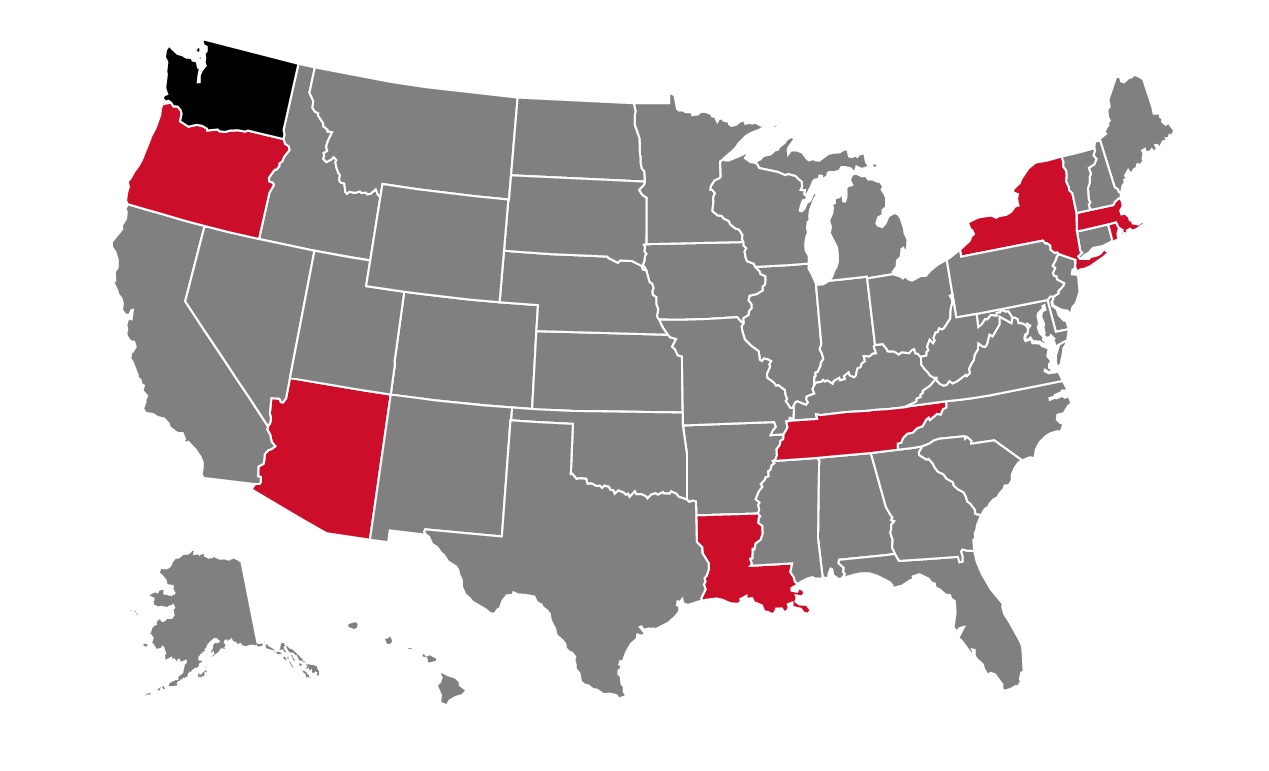
Authorized states are shown in gray, unauthorized states are shown in red and partially authorized states are shown in black.
The College of Nursing is authorized to have a clinical presence in all states, except Arizona, Louisiana, Massachusetts, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island and Tennessee.
In Washington, Master of Science in Nursing and Post-MSN Certificate programs are authorized; Doctor of Nursing Practice programs are not.